Return on investment (ROI)
Compare the income and cost of an investment.
ROI can be expressed by ratio or percentage.
If ROI is more the 0.00 or 0%, its considered as best investment.
It is used to measuring company’s performance whether it is using the sources efficiently or not.
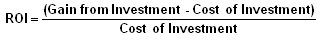
Return on Equity (ROE)
ROE is used to calculating how mach a company earned in comparison to its equity shareholders fund.
Return on Equity (ROE) is one measure of how efficiently a company uses its assets to produce earnings.
It will be expressed in Percentage only.
Return on Equity = Net Income/Shareholder's Equity
Where, Shareholder’s equity = Total Assets- Total liability of the company.
Return on Assets (ROA).
ROA is used to measure the performance of Company’s management.
ROA helps to investors how profitable a company is relative to its total assets.
If a company holds more assets, it can earn more profit. Otherwise it can not earn the high profit.

Asset Turn over Ratio
This ratio is used to calculate company’s revenue for every Rupee of company’s Assets.
Revenue means all sources of income. It includes sales, and other revenues.
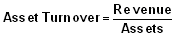
Interest Coverage Ratio
This ratio is very essential for creditors and debenture holders of the company.
A ratio used to determine how easily a company can pay interest on outstanding debt.
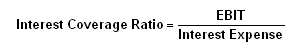
Dividend Payout Ratio
Dividend Payout Ratio is used to calculate how much company has paid the dividend out of its profit.
If this ratio is high means company is one of the well-wisher of investors.


